
Market makers boost liquidity by offering competitive buy/sell quotes for guaranteed shares. Trade confidently with fast order execution and reliable pricing.
Have you ever wondered how transactions in the market happen so smoothly? An intermediary person or company that maintains liquidity is known as a market maker. Market makers are professional traders who play a crucial role in financial markets by providing liquidity and facilitating trading. They are obligated to quote both bid and ask prices for securities, ensuring that a buyer and seller are always available in the market. This helps to maintain market stability and facilitate efficient trading.
Market makers are typically large financial institutions like investment banks and broker-dealers. They have access to significant resources and trading technology, allowing them to provide liquidity in various markets, including stocks, bonds, and derivatives.
Market makers help prevent large price swings and maintain market order by providing liquidity and absorbing market shocks.
How Do Market Makers Operate?
Bid-ask spread and its influence on stock prices
Market makers play a crucial role in determining the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. The bid-ask spread represents the transaction cost traders incur when buying or selling a security.
The bid-ask spread can significantly impact stock prices. A wider spread can increase the cost of trading, reducing investors’ profitability. Conversely, a narrower spread can make it easier for investors to buy and sell stocks, potentially increasing trading activity and liquidity.
Buying and selling securities for their account
Market makers set the bid and ask prices based on their market assessment of supply and demand, as they do when buying and selling for their accounts. They may set a higher ask price if they believe there is a strong demand for a particular security. Conversely, they may set a lower bid price if they believe there is weak demand.
Impact on Stock Prices

Here are some of the impact of market makers on stock prices
- Stabilizing volatile markets: Market makers play a crucial role in stabilizing volatile markets. By providing liquidity and absorbing market shocks, they can help to prevent large price swings and maintain market order. During periods of high volatility, market makers may be more willing to buy or sell securities at wider spreads to maintain liquidity and prevent panic selling.
- How market makers set prices through supply and demand: They set prices based on their assessment of supply and demand in the market. If there is a high demand for a particular security, market makers may raise the asking price to profit from the increased demand. Conversely, if there is a low demand for security, market makers may lower the bid price to attract buyers.
- Role in maintaining liquidity: Market makers play a vital role in maintaining liquidity in financial markets. Providing a continuous market for securities ensures that investors can easily buy and sell their holdings. This liquidity is essential for financial markets’ efficient functioning and helps prevent market crashes.
Market Makers vs. Designated Market Makers (DMM)
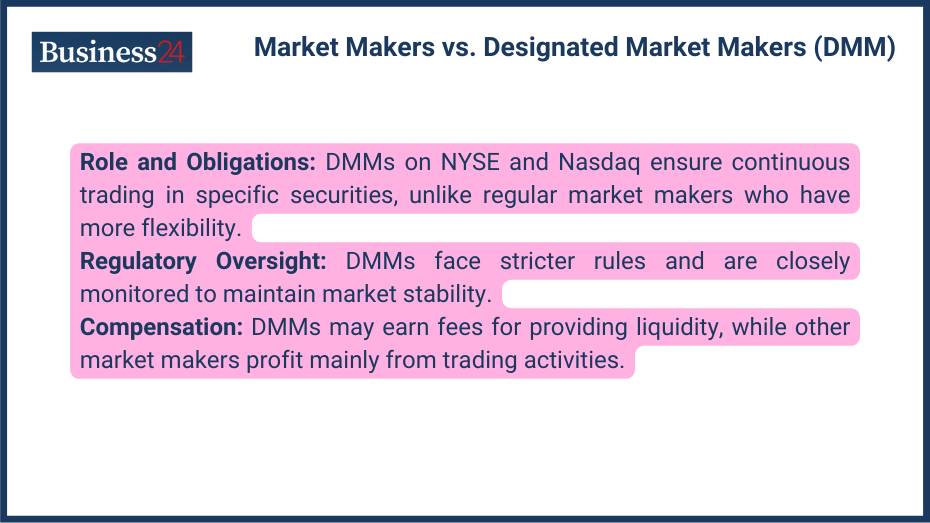
Designated Market Makers (DMMs) are a special type of market maker that operates on certain stock exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq. DMMs are assigned specific securities and are obligated to maintain a continuous market in those securities, even during periods of low trading activity.
While both market makers and DMMs play a similar role in providing liquidity and facilitating trading, there are some key differences in their operations:
- Obligations: DMMs have a more specific obligation to maintain a continuous market in their assigned securities, while market makers may have more flexibility in choosing which securities to trade. DMMs are required to quote both bid and ask prices for their assigned securities at all times, even if there are no other buyers or sellers in the market. This helps to ensure that there is always a market for these securities, even during periods of low trading activity.
- Regulatory Oversight: DMMs are subject to more stringent regulatory oversight than other market makers. The exchange closely monitors them and requires them to adhere to specific rules and regulations. This is because DMMs are critical in maintaining market stability and preventing market manipulation.
- Compensation: DMMs may receive compensation for their services, while other market makers typically earn profits from their trading activities. DMMs may receive a fee for providing liquidity to the market, or they may profit from the spread between the bid and ask prices.
Examples and Global Presence
Many prominent market makers are operating globally, including:
- Citadel: Citadel is a large hedge fund and market maker based in Chicago. It is one of the world’s largest market makers, operating in various markets, including stocks, bonds, and derivatives. Citadel is known for its advanced technology and trading strategies, and it is a major player in the global financial markets.
- Virtu: Virtu is a high-frequency trading firm that provides liquidity to electronic markets. It is one of the largest market makers in the United States and is known for its speed and efficiency. Virtu uses advanced technology and algorithms to identify and execute profitable trading opportunities.
Regional examples from exchanges like London, Tokyo, and Frankfurt
In addition to these global market makers, many regional market makers operate on exchanges around the world. Some examples include:
- London Stock Exchange: The London Stock Exchange is home to some prominent market makers, including BGC Partners and ICAP. These market makers provide liquidity and facilitate trading in various securities, including stocks, bonds, and derivatives.
- Tokyo Stock Exchange: The Tokyo Stock Exchange is one of the largest stock exchanges in the world, and it is home to several market makers. Some of the most prominent market makers on the Tokyo Stock Exchange include Nomura and Daiwa Securities.
- Frankfurt Stock Exchange: This is another major European stock exchange, and it is home to several market makers. Some of the most prominent market makers on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange include Deutsche Bank and Commerzbank.
These are just a few examples of market makers operating around the world. Many other market makers, both large and small, also play a crucial role in providing liquidity and facilitating trading in financial markets.
Disclaimer
eToro is a multi-asset platform which offers both investing in stocks and cryptoassets, as well as trading CFDs.
Please note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 51% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money
This communication is intended for information and educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or investment recommendation. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Copy Trading does not amount to investment advice. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs and makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication, which has been prepared by our partner utilizing publicly available non-entity specific information about eToro.
