
The option is one of the most famous trading instruments, not only from trading but it is used in many strategies in investing also. The option is a high-risk, high-reward type of instrument that can increase your profit and losses. There are different options and trading strategies used by traders and investors, which we are going to discuss in this guide, that can help you adjust or make new options and trading strategies.
What is Options Trading?

Options trading involves buying and selling options contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific underlying asset at a predetermined price by a certain expiry date. Options contracts are mostly used by traders who predict the price trend in a direction or by option writers who want to generate income by depreciating premiums.
The most important thing about options trading is that it provides you leverage. With leverage, you can control a bigger position in the underlying asset with a smaller initial investment than buying the asset.
Options play a significant role in financial markets. As I said, the most use of options is in speculation by traders and investors other than to adjust strategies or for hedging purposes options.
What are Basic Options Trading Strategies?
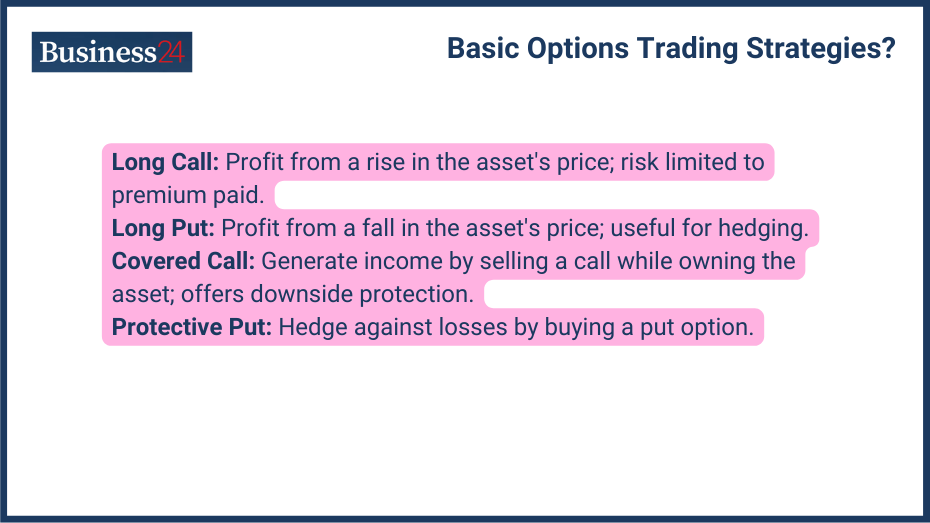
Here are some of the basic options trading strategies:
Long Call and Long Put
- Long Call: Let’s say you predict the price of any asset to rise, and you want to take advantage of the move. In this case, you buy a call option. Buying a call option allows you to profit if the price of the underlying asset increases above the strike price by expiration. You will benefit from the upside while limiting your risk to the premium paid.
- Long Put: Just like in a long call, you expect the price to go up, and in the long put, you expect the asset’s price to go down. If the asset’s price falls below the strike precise before the expiration of the contract, you will profit from the down move. Long put can be used in a bearish market for speculation or to hedge against your portfolio in a downtrend.
Covered Call
In the covered call strategy, you sell a call option while owning the underlying asset. This strategy generates income from the premium received while limiting your potential profit on the stock if the price rises above the strike price by expiration. However, it also protects you from downside risk if the stock price falls.
To implement this strategy, you would first need to buy the underlying stock. Then, you would sell a call option with a strike price at or above the current stock price and an expiration date that aligns with your investment timeframe. This strategy will help you earn extra money with the help of premium decay and also will safeguard you from the downside.
Protective Put
In covered calls, you sell call options to safeguard your investment from the downside, the same purpose for which you buy a put option to hedge your investment. This strategy protects you from potential losses if the price moves in the opposite direction of your holdings.
Let’s say you own 100 shares of NVIDIA. To hedge against a potential decline, you can buy a put option with a strike price slightly below the current stock price. If the stock price falls, the put option gains value, offsetting some of the losses in the stock holding. However, this strategy comes with the cost of the premium paid for the put option.
Which strategy is best for option trading?
There are 100s of options strategies even; you can make one of yours. However, all the options and strategies work in the specific situation. So, naming a best option strategy is not possible because one option strategy cannot work in every situation.
What is the trick for option trading?
Here are some of the tricks and tips you can use in option trading:
- Develop a specific strategy for options trading because the same strategies you use for other methods can’t be directly applied to options trading. Developing a dedicated options strategy can help you gain confidence before making bigger trades.
- Spreads are useful in options trading, which involves buying and selling various options (calls or puts) at different strike prices. This method helps limit potential gains and losses, providing a more controlled risk environment.
- Having an exit plan is equally important as having an entry plan. While experienced traders already know this, beginners must understand it. Never leave a position open without an exit point for both upside and downside scenarios. Avoid second-guessing your decisions and follow your exit plan consistently.
What are Intermediate Options Trading Strategies?
Straddle:
A straddle is an options trading strategy where you buy both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This approach works well if the price of the underlying asset makes a big move in either direction by the expiration date.
Straddles are ideal when you expect high volatility in the asset’s price but aren’t sure which way it will go. This volatility could come from things like earnings reports, economic data releases, or major news events. Because it straddles profit from significant price changes in either direction, it can be a smart way to take advantage of market uncertainty.
Strangle:
A strangle is like a straddle, but it involves buying and selling options with different strike prices. A strangle involves buying both a call option and a put option with different strike prices but the same expiration date. Typically, these strike prices are set above and below the current price of the underlying asset.
Strangles cost less upfront compared to straddles because the strike prices are further from the current price, meaning you pay a lower premium. However, this also means your potential profit is limited compared to a straddle.
The strangle strategy works best when you expect moderate price movements in either direction by the expiration date. Its main advantage is the lower cost, making it a good choice if you anticipate a moderate price change. However, if the price movement is minimal or the price stays the same, you could lose money because of the premiums paid for both options.
Bull Call Spread
A bull call spread is a bullish options strategy in which you buy a call option at a lower strike price and simultaneously sell another call option at a higher strike price with the same expiration date.
Let’s say you are bullish on a particular stock but want to limit your risk compared to simply buying a call option. You could implement a bull call spread. By selling a higher strike call option, you collect a premium that offsets some of the cost of the lower strike call option you buy. This reduces your overall upfront investment.
The profit potential in a bull call spread is limited compared to a long call, but the maximum risk is also capped by the difference between the strike prices of the two call options minus the premium received. This strategy is suitable for situations where you have a moderately bullish outlook on the underlying asset but want to limit your risk.
Bear Put Spread:
A bear put spread is a bearish options strategy where you buy a put option at a higher strike price (long put) and sell another put option at a lower strike price (short put), both with the same expiration date.
If you think a stock will go down but want to limit your downside risk, you can use a bear put spread instead of just buying a put option. By selling the lower strike put option, you collect a premium that reduces the cost of the higher strike put option you buy. This lowers your upfront investment.
While the profit potential is limited compared to just buying a put, your maximum risk is capped by the difference between the strike prices of the two put options minus the premium you received. This strategy works well when you have a moderately bearish outlook on the stock and want to limit your risk.
What are Advanced Options Trading Strategies?

Iron Condor:
An iron condor is a neutral options strategy involving four legs:
- Selling a call option at a higher strike price (short call)
- Buying a call option at an even higher strike price (long call)
- Selling a put option at a lower strike price (short put)
- Buying a put option at an even lower strike price (long put)
All options have the same expiration date.
If there is low volatility or flat price movements in the underlying asset price, you can use the Iron Condor strategy. The profit you get is from selling the two outer call and put options. The maximum risk is capped by the difference between the strike prices of the inner call and put options minus the total premium received. However, if the price moves big in either direction, you can suffer a loss.
Butterfly Spread:
A butterfly spread combines elements of bull and bear spreads with a common strike price. There are two variations: bull butterfly and bear butterfly.
Butterfly spreads offer a defined risk and profit potential. They are used when you have a neutral to slightly bullish or bearish outlook on the underlying asset price and anticipate limited volatility.
- Bull Butterfly Spread: In Bull Butterfly Spread, you buy a call option at a higher strike price, sell two call options at a middle strike price, and buy another call option at a lower strike price. The profit is capped and comes from the difference between the premiums received from selling the two middle calls minus the premiums paid for the outer calls.
- Bear Butterfly Spread: Bear butterfly spread involves buying a put option at a lower strike price, selling two put options at a middle strike price, and buying another put option at a higher strike price.
Calendar Spread
A calendar spread involves buying and selling options contracts with the same strike price but different expiration dates. There are two variations: bull calendar spread and bear calendar spread.
Calendar spreads are used to take advantage of time decay. They offer a lower upfront cost compared to buying a single option with a longer expiration.
What are the Key Terminologies in Options Trading?
- Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The specific date by which the option contract must be exercised; otherwise, it expires and becomes worthless.
- Premium: The cost of purchasing an options contract.
- Intrinsic Value: The difference between the current market price of the underlying asset and the strike price of the option. An in-the-money (ITM) option has positive intrinsic value, while an out-of-the-money (OTM) option has no intrinsic value but may still hold time value.
- Time Value: Time value diminishes as the option approaches expiration due to time decay. Options contracts derive most of their value from time value early in their lifespan.
How to Manage Risks in Options Trading?
Options are leveraged instruments, and risk management is very important in trading options because it has the capability to wipe your capital in your early days. Here are some of the easy you can manage your risk in options trading:
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
As a trader, stop loss is the most important tool that saves you from cutting your loss early and saves your capital. Stop-loss orders help limit losses by automatically exiting your options position at a predefined level. Sometimes, backfires against your position can happen, and stop-loss orders can help you from moving against your position.
Stop-loss orders can be used for both long and short options positions. For example, with a long call option, you might set a stop-loss order below the strike price to limit potential losses if the underlying asset price falls. Similarly, for a short put option, you might set a stop-loss order above the strike price to limit losses if the asset price rises significantly.
Hedging Techniques
Options are an important tool for investors, too, because they can be used to hedge existing holdings and protect against losses. For example, an investor holding a long position in a stock can buy a put option to hedge against a potential decline in the stock price.
Protective puts is one of the examples of an options strategy used for hedging stock holdings. Other hedging strategies using options include bull put spread, bear call spread, collar, etc.
Position Sizing
Position sizing is the amount of capital you allocate to each options trade. Putting too much into a single trade can disbalance your risk management, and too small can lower your profits.
The most common approach to position sizing is to allocate a fixed percentage of your total trading capital to each trade. This percentage can vary depending on your risk tolerance and the specific options strategy you’re using.
Educational Resources and Tools
Look for reputable sources written by experienced options traders or financial professionals. These resources can provide in-depth knowledge about options contracts, various strategies, risk management techniques, and practical applications.
Several online platforms offer structured courses and tutorials specifically designed to teach options trading strategies. These can provide a valuable learning experience for beginners or those seeking to enhance their knowledge.
Many online brokers and financial websites offer options calculators and trading simulators where you can practice and test different options writing strategies before risking real capital.
Here are some online resources you can use:
- Options Industry Council (OIC): https://www.optionseducation.org/ (Provides educational resources and certification programs for options traders)
- Investopedia Options Simulator: https://www.investopedia.com/simulator/
- TD Ameritrade OptionsPlay:
https://www.schwab.com/trading/thinkorswim/guestpass (Options trading simulator)
Disclaimer
eToro is a multi-asset platform which offers both investing in stocks and cryptoassets, as well as trading CFDs.
Please note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 51% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money
This communication is intended for information and educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or investment recommendation. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Copy Trading does not amount to investment advice. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs and makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication, which has been prepared by our partner utilizing publicly available non-entity specific information about eToro.