
A brokerage fee is a charge applied by brokers for executing transactions or offering specialized services, such as buying, selling, or financial consulting.
Before you understand a brokerage fee, you must know what a broker is. A broker is someone who works as an intermediary between exchanges and users. So, let’s say you want to buy a stock. You have to put the order to your broker, and the broker will complete the transaction for you in exchange.
A brokerage fee is a charge imposed by a broker for executing that transaction or providing specific services on behalf of a client. These fees can vary widely depending on the type of transaction, the brokerage firm, and the specific services rendered.
Types of Brokerage Fees (Trading Fees vs. Non-Trading Fees)

Brokerage fees can be categorized into two primary types:
- Trading Fees: When you buy or sell securities through your broker as the service charge, he will charge a trading fee. These trading fees can be commission-based, flat-fee, or volume-based.
- Non-Trading Fees: Non-trading fees are unrelated to specific trades but are associated with account maintenance, data services, or other value-added services provided by the brokerage. Non-trading fees are generally yearly or quarterly, paid once by the user for the service.
What is a normal brokerage fee?
It depends on what brokerage service you are using or what asset you are trading. Traditional brokerage houses charge more brokerage fees because they offer a wide range of services, while discount or online brokers offer lower fees. There are various broker houses, and the range of broker fees is also wide.
What is the History of Brokerage Fees?
Brokers and brokerage fees are not new; they have been with us for centuries, and over the years, there have been major changes. Historically, brokers charged a substantially high brokerage for executing trades because of the manual process involved. New technology and automation have heavily impacted brokerage rates and have seen a huge decline. Also, In recent times, the introduction of commission-free brokerage models has disrupted the industry, forcing traditional brokers to adapt their fee structures.
Technology has significantly reduced brokerage fees due to ease and automation. Online trading platforms, algorithmic trading, and automation have made the trading process more efficient, cutting operational costs for brokerages, and investors now pay lower fees. Moreover, technology gives investors access to real-time market data and trading tools, helping them make better investment decisions.
What is the Average Brokerage Fee?
As I said earlier, brokerage fees vary according to the region, asset, service, and type of broker used. In the UK, the average brokerage fee for online trading platforms typically ranges from £4 to £12 per trade. You can also find brokers according to your needs; some platforms may offer lower fees for frequent traders or higher fees for additional services.
Here is the average brokerage fee depending on the region:
| Country | Average Brokerage Fee per Trade | Notes |
| USA | $5 – $10 | Some brokers offer commission-free trades. |
| UK | £4 – £12 | Fees can vary based on trading frequency and additional services. |
| Germany | €5 – €15 | Fees depend on the broker and the type of trade (domestic or international). |
| Australia | AUD 10 – AUD 20 | Fees vary by broker and the size of the trade. |
| Canada | CAD 5 – CAD 10 | Some brokers offer discounted rates for frequent traders. |
| Japan | ¥500 – ¥1,000 | Fees vary based on the broker and the size of the trade. |
What are the Different Types of Brokerage Fees?
Different types of brokerage fees:
- Commission-Based Fees
In the initial days, traditional brokerage houses charged customers commissions based on the value of the trade. Boker benefits from this type of brokerage fee for its service and expertise in the market. However, due to advancements in technology, commission-based fees have become less common. For example, today, the standard commission for full-service brokers is between 1% and 2% of a client’s managed assets.
- Flat Fees Per Trade
Flat fees per trade are one of the most common brokerage methods used nowadays. Many online brokerages charge a flat fee for each trade, regardless of the trade size. This fee structure provides transparency and predictability for investors. For example, in the US, the most common flat fee per trade is $5.
- Volume-Based Fees
Some brokerages offer tiered fee structures based on trading volume. Investors who trade frequently may qualify for lower fees per trade. Those who trade frequently and in high volume can benefit from the volume-based fees. Interactive Brokers offers a tiered brokerage model ranging from $0.0005 to $0.0035 per share.
- Hidden Fees to Watch Out For
Beyond explicit trading fees, investors should be aware of potential hidden fees. These can include account maintenance fees, inactivity fees, data fees, platform fees, and fees for specific order types. You must check all the documents carefully and review a brokerage’s fee schedule before opening an account.
What are the Fees Charged by Top Brokerages?
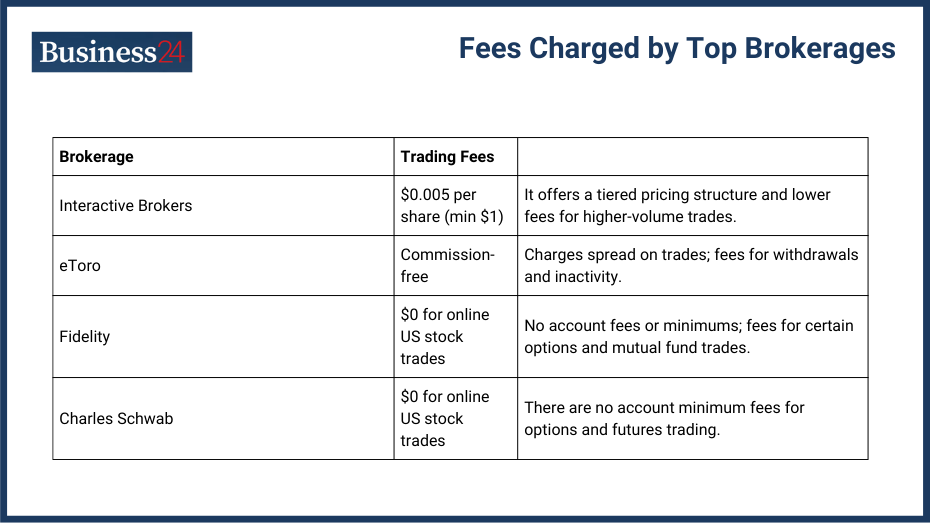
Major brokerages offer diverse fee structures to cater to different investor profiles. Here are the examples of major brokerages:
| Brokerage | Trading Fees | |
| Interactive Brokers | $0.005 per share (min $1) | It offers a tiered pricing structure and lower fees for higher-volume trades. |
| eToro | Commission-free | Charges spread on trades; fees for withdrawals and inactivity. |
| Fidelity | $0 for online US stock trades | No account fees or minimums; fees for certain options and mutual fund trades. |
| Charles Schwab | $0 for online US stock trades | There are no account minimum fees for options and futures trading. |
No one would have thought that there would be commission-free brokers, but advancements in technology and fewer manual processes have made it possible. Although these brokers don’t charge commissions for stock and ETF trades, they still make money in other ways. They might earn interest on your cash balances, get paid for directing your orders, or charge fees for options trading and other products.
What are the Advantages of Low Brokerage Fees?
Advantages of low brokerage fees:
- Cost Savings for Frequent Traders
Scalpers and Intraday traders place many buy and sell orders in a day, and if the brokerage fees are high, the brokerage from frequent trades can mount up to a large amount. But if they are paying low fees, they can retain a larger portion of their profits. Small profits can be eaten by fees if they are high, and despite being profitable, a trader will close flat or slightly negative.
- Impact on Investment Returns
Lower brokerage fees directly contribute to improved investment returns. In the past, brokerage fees were high, so investment return was reduced due to them. Over time, even small reductions in fees can have a substantial impact on an investment portfolio’s overall profitability. By minimizing costs, investors can reinvest savings and earn compounding benefits.
- Benefits for Small Investors
Low brokerage fees are particularly beneficial for small investors with limited capital. By reducing the percentage of their investment allocated to fees, they can maximize their exposure to the market and potentially achieve better long-term returns.
What are the Disadvantages of High Brokerage Fees?
- Reduced Profit Margins
If high brokerage fees are associated with a trade, you have to make more profit to cover the fees because a small profit will be seen as flat due to a reduction in the brokerage fees. Frequent traders are most impacted by the high brokerage fees because they have to place tens of trades every day.
- Impact on Long-Term Investment Growth
The cumulative effect of high brokerage fees can be substantial over the long term. By reducing the amount invested, high fees can hinder an investment portfolio’s growth potential. This is particularly relevant for investors who adopt a buy-and-hold strategy.
- Increased Transaction Costs
High brokerage fees can discourage investors from making frequent trades, even if it’s in their best interest. This can limit investment flexibility and potentially hinder the ability to capitalize on market opportunities.
What are the Investment Strategies Related to Brokerage Fees?
Choosing the Right Brokerage for Your Investment Style
Write down all your needs and goals regarding your investment and accordingly select a brokerage that aligns with your investment goal and trading frequency. For example, for active, intraday, or scalpers, a low-commission or commission-free broker is the best option. However, investors who want research and advisory services or other wide range of benefits may choose a full-service broker.
Using Fee Calculators to Compare Brokerages
There are hundreds of brokers available, and it is hard to compare them one by one. To effectively compare brokerage fees, investors and traders can use free calculators that compare the brokerage of different firms; various financial websites or brokerage platforms provide these calculators. These tools allow investors to estimate the total cost of ownership based on their trading volume and investment preferences.
Tips for Reducing Trading Costs
Investors can cut down on brokerage fees with a few smart strategies. Combine trades to reduce costs, opt for limit orders instead of market orders, and check out discount brokerages. It’s also important to understand your broker’s fee structure and look for ways to save.
What are the Regulatory and Market Dynamics of Brokerage Fees?
The brokerage industry is subject to various regulations that impact fee structures. Regulatory bodies oversee investor protection, fair competition, and market integrity. Changes in regulatory policies can influence brokerage fees, either by imposing new costs or creating opportunities for cost reductions.
The brokerage industry is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing investor preferences. The trend towards lower fees is likely to continue, with more brokerages offering commission-free trading or tiered fee structures.
What is the Difference Between Brokerage Fees and Other Investment Costs?
Comparison with Mutual Fund Fees and ETF Expenses
While brokerage fees are associated with executing trades, mutual fund fees and ETF expenses are ongoing costs associated with owning these investment vehicles. Mutual funds typically charge management fees, expense ratios, and load fees, while ETFs generally have lower expense ratios.
Differences Between Brokerage Fees and Robo-Advisor Fees
Robo-advisors charge a management fee based on the value of the assets under management. This fee covers portfolio management, rebalancing, and other services. Brokerage fees, on the other hand, are transaction-based costs. Investors should compare the total cost of ownership for both options to determine the most suitable approach.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Brokerage fees are crucial for investors because they affect your investment returns. To get the most out of your investments, you should understand the different types of fees, compare various brokerage options, and find ways to save on costs. By carefully looking at fee structures and picking the right brokerage, you can optimize your portfolio and reach your financial goals.
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between a full-service broker and a discount broker? Full-service
- Full-service brokers offer financial advice and personalized help and assistance, but their brokerage fees are high. Discount brokers focus on trading at lower costs and provide less personalized assistance than full-service brokers.
Q. How do I calculate the total cost of ownership for a brokerage account? Add up trading
- To calculate the total cost of ownership of a brokerage account, you have to calculate the different costs associated with the account, such as fees, account maintenance fees, inactivity fees, data fees, and other charges.
Q. What are the best practices for managing brokerage fees?
- Shop around for the best brokers, consider discounts, consolidate trades, use fee-free options, and negotiate.
Q. Are there any hidden fees associated with commission-free brokerage accounts?
- Yes, check for any hidden fees associated with commission-free brokerage accounts. Check for account maintenance, inactivity, data, and other fees.
Q. How can I find a reputable brokerage firm?
- Check for licenses, read reviews, assess reputation, review services, and compare fees.
Disclaimer
eToro is a multi-asset platform which offers both investing in stocks and cryptoassets, as well as trading CFDs.
Please note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 51% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money
This communication is intended for information and educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or investment recommendation. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Copy Trading does not amount to investment advice. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs and makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication, which has been prepared by our partner utilizing publicly available non-entity specific information about eToro.