
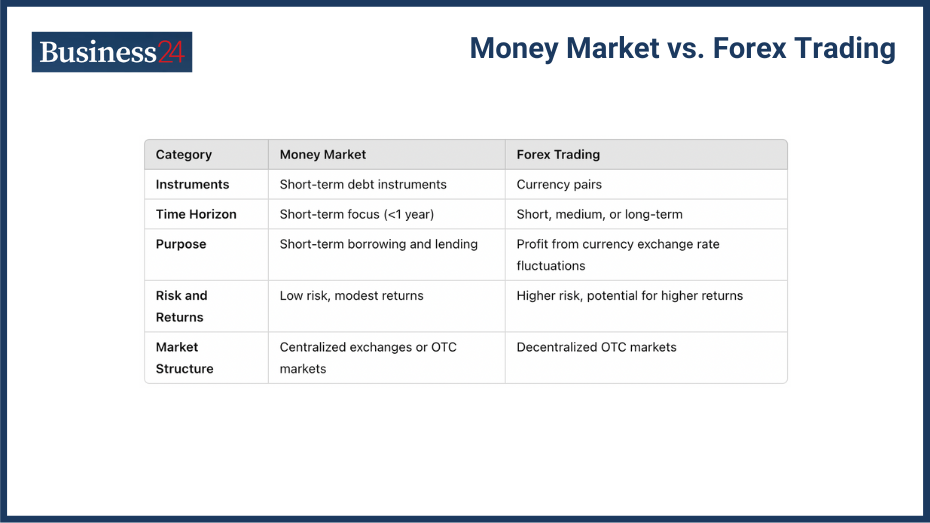
Currency trading, or forex trading, involves exchanging one currency for another at an agreed price. The end goal is to make profits from this exchange of currencies.
The global currency or forex market is one of the largest in the world with over $6 trillion worth of value exchanged in a single day. The global currency market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week which is rather unique for markets.
How is Currency Trading Different from Forex Trading?
Currency trading and forex trading are often used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences in their contexts and applications.
Overview of Currency Trading
Currency trading broadly refers to the exchange of currencies in various contexts, including retail transactions. Current trading is, therefore, a broader terminology and applies to all transactions irrespective of the size of the transaction involved or the nature of the transacting parties.
Retail traders involve individual traders who are looking to get a piece of the action. They use online brokerage apps to trade directly with each other instead of being involved with banks and other financial institutions.
However, retail currency trading is also used interchangeably with the term retail forex trading.
Overview of Forex Trading
Forex trading specifically refers to the decentralized global market for trading national currencies against each other. This usually involves brokers dealing with each other to make profits.
If we consider retail trading like Over The Counter (OTC) trading as retail forex trading, the two terms are exactly alike, and there is nothing that separates them. However, if retail trading is considered apart from forex trading, as some analysts do, then currency trading is a wider market that covers both retail and forex trading elements.
How Has Currency Trading Evolved Over Time?
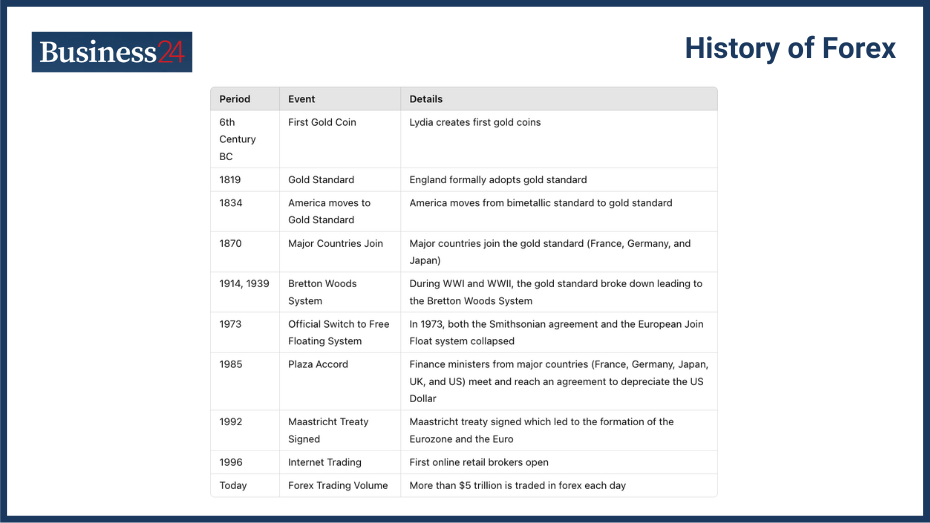
Currency trading has evolved from ancient barter systems to a sophisticated global financial market. Currency trading aka forex trading is now the biggest liquid market in the world with over $6 trillion worth of transactions carried out on a daily basis.
Origins of Currency Exchange
Currency trading began with ancient barter systems and evolved through various forms of trade. Initially, the barter system meant there was no requirement for an intermediate source of value, aka currency. Traders would barter their goods for other goods in the market, but that proved to be a difficult task. This led to the usage of precious metals like Gold and Silver as means of exchange, aka currency.
Gold, Silver, and other metals have been used as currency for a long time. However, coinage only started in the 6th century BC. Gold, Silver, and sometimes Bronze coins were used. This led to the start of the first currency trading in busy markets across busy trade routes and markets in the more advanced parts of the world.
Paper money was introduced in China before the 10th century AD. It was basically a receipt for Gold or Silver. Famous Italian explorer Marco Polo reportedly took the idea to Europe, and paper currency became dominant during the 16th and 17th centuries. It simplified the use of currency to a large degree. However, the currency was always backed by Gold, and if a country’s treasury was unable to repay paper notes in equivalent precious metal, it was considered bankrupt, and its currency crashed quickly enough.
Key Developments in Modern Forex Markets
Modern forex markets developed significantly after the Bretton Woods agreement and the shift to floating exchange rates. The agreement was struck after World War II. The United States of America had emerged victorious in the global war and wanted to make the Dollar the reserve currency of the world. The Bretton Woods agreement meant that the world’s national currencies would be pegged to the greenback. This led to the development of the global forex/currency market that we see today.
The currency trade started to explode in numbers after American President Richard Nixon ditched the Gold standard in 1971. While it did result in the devaluation of the dollar against precious metals, it cemented the former’s status as the world’s reserve currency and helped the USA remain the dominant economic force in the world.
With time, paper money disappears as things get more and more digital. With the increasing digital existence, the forex market has also grown considerably over time, especially as currencies have become increasingly volatile.
What are the Different Types of Currency Trading Markets?
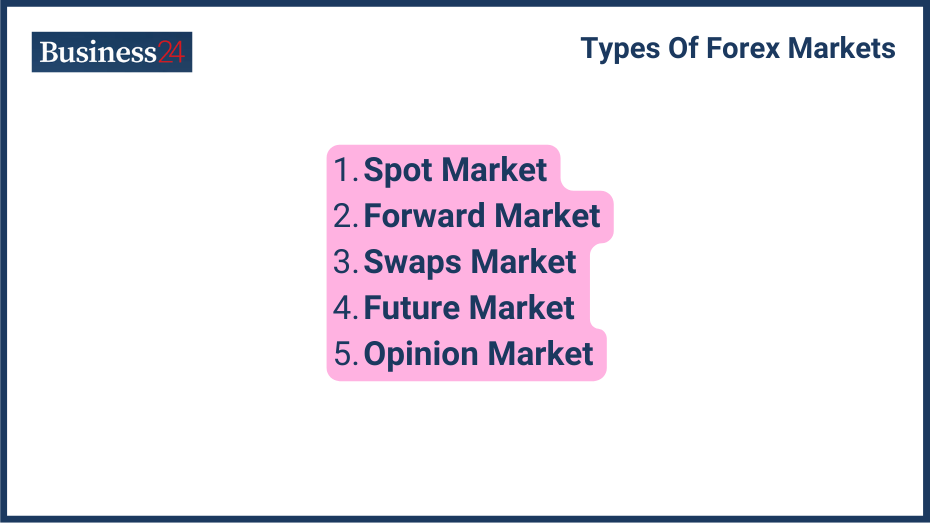
The main types of currency trading markets are spot, forward, and futures markets.
Spot Market Operations
Sometimes called “cash currency trading,” the spot market is the largest sector of the forex market. Currencies are always traded in pairs or in one currency for another, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/CAD. The margins are smaller than futures, but the liquidity is considerable, thus allowing space for profits.
Forward and Futures Markets
Forward and futures markets allow traders to buy and sell currencies at predetermined future dates and prices. The futures market requires traders to buy/sell a currency pair in the future at a pre-determined rate. If any party cannot pay, they are required to pay a fine called the premium, which is also pre-set.
Forward currency trading on the other hand is a customized futures agreement. Rather than agreeing to a rigid futures agreement with no variables, institutions can join together and make Over The Counter (OTC) agreements with each other. Forward currency trading is normally used by companies and financial institutions for hedging. Hedging is a means to protect parties from the unpredictability and volatility of the forex markets.
Which Factors Influence Currency Values?
Currency values are influenced by economic indicators, political stability, and market dynamics.
Economic Indicators Impacting Forex
Key economic indicators impacting forex include GDP, interest rates, and inflation. Forex is a decentralized market overall, but the centralized financial decision-making by governments affects it the most. Here is how these government policies impact Forex:
GDP: GDP is the total value of goods or services produced by a country’s economic sector in a single year. When it comes to the forex markets, GDP growth and GDP value are both important indicators. If a country’s GDP growth is consistently strong, the demand for its current is expected to be consistent even if its total GDP value isn’t so high. If a country’s GDP value is among the very top, short-term growth problems don’t immediately translate into a weakening of its currency.
Interest Rates: If a country’s interest rates are on the higher side, the international/national demand for its currency will be high and vice versa.
Inflation: If a country has high inflation rates, the value of its national currency decreases and vice versa. This is because the said country is printing too much money to cover its deficits.
Other economic factors impacting forex include trade, manufacturing activity, and employment data.
Political Conditions Affecting Currency Trading
Brief: Political events and economic policies can significantly impact currency trading. As a general rule, peaceful, economically strong countries have strong currencies, while war-torn, poor countries have weak currencies.
Impact of Market Sentiment on Currency Values
Market sentiment, driven by news, events, and trader behavior, can cause fluctuations in currency values. It is driven by various market forces, including forex brokers and the news cycle. The market sometimes anticipates certain actions beforehand and impacts the national currency directly. Both optimistic and pessimistic market sentiments are present in the market.
How Can You Analyze the Forex Market?
Forex market analysis involves technical and fundamental analysis methods. You can use these tools to analyze the Forex market:
Technical Analysis in Forex
Technical analysis uses charts and indicators to predict future currency price movements.
Traders use price charts and various technical indicators to make a move before the next situation presents itself.
Typical price charts include:
- Line graph
- Bar graph
- Candlestick graph
Typical mathematical technical indicators include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI)
- Bollinger Bands
- Moving Averages
Typical technical analysis includes support and resistance level analysis, pattern recognition, and trend analysis. Technical analysis is useful but it is not a fool-proof method of predicting the future.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex
Fundamental analysis assesses economic indicators and news events to forecast market trends. Fundamental analysis is important as it gives a bird’s eye view of the macro-economic relative situation of the two countries. This helps currency/forex traders have a better grasp of the situation and make educated guesses about the future of the currency pair.
Sometimes, global news also creates an impact on currency pairs, such as the Covid-19 pandemic or other similar natural disasters.
Using Sentiment Indicators
Sentiment indicators reflect the overall mood of traders and can provide insights into potential market movements. Typical sentiment indicators include:
- Social Media Analysis:
- Commitment On Traders (COT):
- Market Speculation Data:
- Volatility Analysis:
What are Basic Currency Trading Strategies for Beginners?

Basic currency trading strategies for beginners include day trading and swing trading.
Day Trading Strategies
Day trading involves making multiple trades within a single trading day.
Swing Trading Techniques
Swing trading takes advantage of market price swings over several days.
Position Trading Approaches
Position trading involves holding trades for longer periods to profit from major price trends.
What are Common Challenges in Currency Trading, and How Can They Be Overcome?
Common challenges in currency trading include managing risk and overcoming psychological hurdles.
Risk Management Techniques
Risk management techniques include using stop-loss orders and setting trading limits.
Overcoming Psychological Hurdles
Managing emotions and maintaining discipline are key to overcoming psychological hurdles in trading.
Common Mistakes by Beginner Traders
Common mistakes include overtrading, not using stop-losses and emotional trading.
What Advanced Techniques Can Improve Your Forex Trading Skills?
Advanced forex trading techniques include scalping and using leverage wisely.
Scalping in Forex
Scalping involves making quick, small trades to capture small price movements.
Using Leverage Wisely
Leverage should be used carefully to amplify gains while managing potential risks.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading uses computer programs to execute trades based on predefined criteria. These are sometimes called trading bots and they are able to execute trades at a high speed. They are also considered risky overall because of the threat of cyber attacks and the presence of bugs.
What Tools and Resources are Essential for Forex Trading?
Essential tools for forex trading include the right trading platform and educational resources.
Choosing the Right Trading Platform
The right trading platform offers reliability, user-friendliness, and robust features.
Educational Resources for Currency Trading
Educational resources include books, online courses, and reputable websites.
Best Forex Trading Apps
Forex trading apps provide convenience and functionality for trading on the go.
How Do You Start Your Journey in Currency Trading?
To start currency trading, educate yourself, set up a trading account, and develop a strategy.
First Steps in Currency Trading
Begin with learning the basics, choosing a broker, and practicing on a demo account.
Developing a Trading Plan
A trading plan includes setting goals, risk management strategies, and trading rules.
Trading plans need to be clearly set for the future.
Choosing a Forex Broker
Important factors include the broker’s reputation, fees, and trading platform features.
The main aspects to consider while choosing a Forex broker include:
- Regulatory Standing: The Forex broker in question needs to be registered with the relevant Forex regulator. If not registered, you may have limited legal recourse if you are scammed.
- Track Record: Research the track record of the Forex broker in question on online forums and also through word of mouth. Any red flags in previous operations need to be identified.
- Use Experience: View user testimonials and check out the platform’s usability. Identify any shortcomings.
- Fee Structure: Brokers need to be clear about the kind of fees they are charging. You can compare the fee structures of different platforms.
What are Essential Definitions in Currency Trading?
What is the definition of a Currency Pair?
A currency pair is the relative value of one currency pair over another, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, or USD/CAD. Generally, the currency with historically greater value is in the numerator, and the one with lesser value is in the denominator. Forex or currency trading is only done in currency pairs.
What is the definition of Leverage in Forex?
Leverage in Forex allows investors to gain the impact of a much larger sum than their invested capital. It is often like 2x, 5x, 10x, or 100x. Leverage is also available in other markets like crypto and the stock exchange, but it is a double-edged sword overall. It is considered extremely risky.
What is the definition of a Pip?
A pip is the basic unit of spread in Forex trading. If a currency pair is bought at 1.3001 and sold at 1.3001, then the spread is one pip.
What is the definition of Spread in Forex?
The spread is the difference between the buying and selling price of a currency pair. It is measured in pips, which is essentially the Forex dealer’s margin. The greater the spread, the more volatile the currency becomes.
What is the definition of a Forex Broker?
A Forex broker is a platform that acts as the middleman between the trader and the Forex market itself. They include retail traders and institutional traders.
What is the definition of Margin in Forex?
Margin is the amount submitted in leverage trading. Investors can go 2x, 5x, 10x, 20x, or even 100x on the margin amount, but it is a risky endeavor.
What is the definition of a Lot in Forex trading?
A lot is a standard unit of the amount of base currency in the exchange pair. A nano lot has 100, a micro lot has 1000, a mini lot 10,000 and a standard lot has 100,000 units.
What is the definition of Technical Analysis in Forex?
Technical analysis is the use of certain indicators to analyze graphs and identify patterns to predict the future of currency trading pairs.
What is the definition of Fundamental Analysis in Forex?
The definition of fundamental analysis in Forex is to use the current news cycle and economic indicators to predict the future outlook of a currency pair. If the base currency’s native country is going through a rough patch and the other is somewhat better, the trading pair will go down and vice versa.
What are the Most Frequently Asked Questions About Currency Trading?
Addressing common and specific queries about currency trading provides clarity and helps beginners understand the nuances of the market.
How Much Capital Do You Need to Start Trading Currencies?
Currency trading markets don’t have a hard-and-fast minimum amount set for investors. Each broker’s minimum deposit is different and generally hovers around the $100 value.
Can You Trade Currency on a Mobile Device?
Yes, almost all top currency trading platforms now offer mobile apps for trading purposes.
What Are the Tax Implications of Currency Trading?
Currency trading activity needs to be reported to the government tax department. Capital Gains Tax (CGT) is to be filed for all profits derived from currency trading.
How Do You Keep Up with Forex News and Trends?
You should follow the news sector extensively to analyze the market. You should also read and remain up-to-date through business reporting platforms like Forbes, Bloomberg, etc.
Is It Possible to Make a Living from Currency Trading?
Yes, with the right approach, it is possible to make money from currency trading. But, it requires a strong trading strategy based on a thorough understanding of the market.
Conclusion: Is Currency Trading Right for You?
Currency trading offers significant opportunities but requires a solid understanding of market dynamics, risk management, and personal commitment. The currency market needs solid technical and fundamental analysis for accurate predictions of the future. Selecting the right currency trading broker is important for the future. As is the selection of a robust trading strategy that minimizes risk and prioritizes sustainable profits. Currency trading is often used interchangeably with Forex trading but there can be subtle differences between the two. .
Disclaimer
eToro is a multi-asset platform which offers both investing in stocks and cryptoassets, as well as trading CFDs.
Please note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 51% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money
This communication is intended for information and educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or investment recommendation. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Copy Trading does not amount to investment advice. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs and makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication, which has been prepared by our partner utilizing publicly available non-entity specific information about eToro.
