
Leverage in forex trading refers to using borrowed capital to increase the potential return on investment. The main goal is to magnify profits with this extra capital, but leverage is a double-edged sword for both parties as it carries significant risk and could bankrupt entire trading platforms on its own.
How Does Leverage Work in Forex?
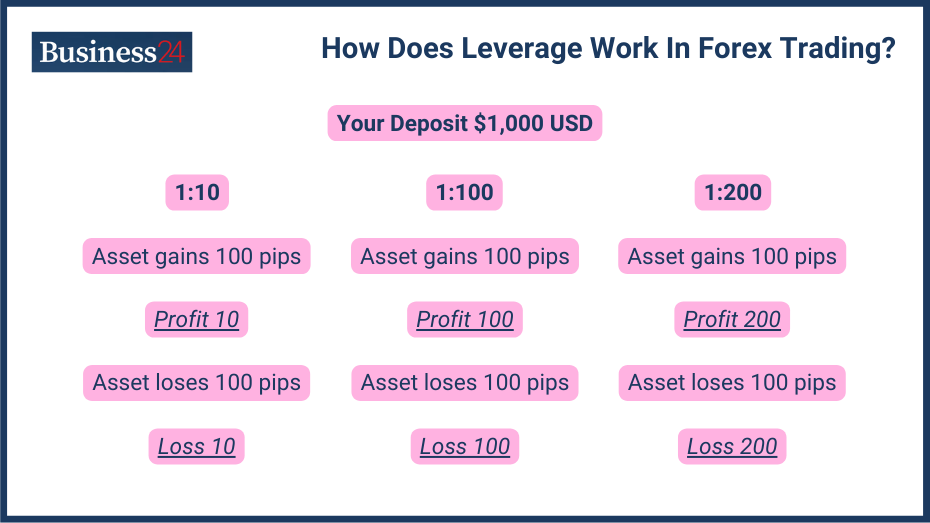
Leverage allows traders to gain a larger exposure to the forex market than the amount of their initial investment. Leverage is increasingly popular with traders because it offers the lure of higher profits. Here is how it works:
- Leverage is offered in the form of ratios like 2:1, 5:1, 10:1, or even higher. With a 10:1 ratio, you can trade $10 for every $1 of margin you deposit.
- If you incur a profit, most of it goes to you, while the platform charges a margin fee for each trade.
- If you incur a loss, you lose your initial investment first and then start to accrue debt.
- Higher leverage is only offered to more experienced/successful traders, and you can only start with smaller margins.
Why is Leverage Important in Forex Trading?
Leverage is crucial for amplifying profits in forex trading but also increases the potential for higher losses. While it is available in all major markets, including the stock market, crypto, and commodities, leverage holds extra appeal in the Forex markets because of its low volatility. Traders have two choices to increase their profit margins dramatically: invest larger amounts or appear to have larger capital through leverage.
Leverage also allows Forex traders increased flexibility, allowing them to dip into multiple markets and diversify their market positions with position sizing.
What are the Risks of Using Leverage in Forex?

While leverage can significantly increase potential returns, it also raises the risk of substantial losses. Traders need to consider these significant risks when using leverage in Forex trading.
Examples of Leverage-Induced Failures
There are several cautionary case studies of leverage-induced failures in Forex trading. Due to privacy concerns, exact details remain hidden from the public eye, but back in 2015, the Swiss National Bank (SNB) suddenly decided to remove the Swiss Franc (CHF) peg with the Euro (EUR). As a result of this sudden move, several billion dollars worth of leveraged positions of hedge funds were reportedly adversely affected and resulted in considerable losses. This is despite both the Euro and CHF being relatively safe bets in the Forex markets.
Managing Leverage Risks
To manage leverage-related risks, traders should employ the following strategies:
- Start small: Never start with highly leveraged positions. Start small by dipping your toes in the market and then slowly increasing the leverage if it becomes profitable.
- Stop-loss Orders: These orders allow your position to be liquidated if a certain price level is breached.
- Analyze Risk-reward Ratio: Focus on trades with a reasonable risk-reward ratio. With leverage, you have already increased your risk considerably, so it is time to focus on less risky trades.
How to Calculate Leverage in Forex Trading?
Calculating leverage involves determining the ratio of total exposure to actual trading capital.
Practical Calculation Examples
Leverage calculation is relatively simple, but there are certain terminologies to remember:
Total Position Size: This is the total position in the market with leverage factored in.
Equity: This is the original investment of the trader plus/minus profits/losses.
Leverage can be calculated by dividing the total position size by equity or total position size/equity.
For example, if you have $1,000 and wish to engage in a 10:1 leverage, the total position size is around $10,000. You use $10,000 to buy 9,200 EUR with a EUR/USD exchange rate of 1.0869. If the EUR rises 5% against the USD, the EUR/USD exchange rate rises to 1.1412, and you liquidate for roughly $10,500. Initially, the leverage was 10:1, but with profits, it has lowered to $10,500/$1500=7 or 1:7. So, you have gained $500 or 50% in value of your initial investment.
Conversely, we have to consider a loss-reporting scenario.
For example, if you have $1,000 and wish to engage in a 10:1 leverage, your total position size is around $10,000. You use $10,000 to buy 9,200 EUR at a EUR/USD exchange rate of 1.0869.
However, this time, the currency falls by 5%, and you are forced to liquidate for $950.
Now, the total leverage has increased to 9500/500 19:1. You will need to pay back the difference to the broker, and if you can’t, you are officially bankrupt.
How Can Traders Manage Risk with High Leverage?
Effective risk management strategies are essential when trading with high leverage to safeguard investments.
Tools for Risk Management
To minimize risks associated with leverage, you need to take the following steps:
- Managing Financial Exposure: To minimize market exposure, you need to manage your financial exposure. This includes diversifying your forex investments in less-risky trading pairs, position sizing, and risk tolerance assessment.
- Leverage Calculators: To asses risks associated with leverage, use leverage calculators from different forex websites. They are generally free to a certain degree.
- Risk Assessment Software: Use professional forex risk assessment software from companies like Bound, Marketbulls, Kyriba, and others.
What is Margin, and How is it Related to Leverage?
Margin is the amount of capital required in an account to maintain a forex trade with leverage.
Understanding Margin Requirements
Margin is the deposit traders must put up to engage in leverage trading. It is used as collateral for leveraged positions. Margin requirements are present on major Forex trading platforms for different trading pairs. If a trading pair has a 10% margin, you can engage in 10x the value of your margin.
Major trading pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD are relatively stable, so margin requirements are much lower. Users can trade with as low as 5% margin. However, exotic pairs with unstable patterns require more than a 10% margin value.
Investors only need to pay interest on the extra capital borrowed on top of the margin.
Margin Calls: What Happens When Things Go Wrong
Brokers enforce certain rules for leverage/margin trading. If the value of your leveraged assets falls below a certain level, it leads to an event called a margin call. This is when the exchange freezes your assets, so you need to deposit more or sell your remaining positions.
Margin calls occur when a trading pair loses value quickly enough, resulting in big losses for traders working with leveraged positions.
Essential Definitions in Forex Trading
What is the definition of Leverage?
Leverage is when a trader borrows money from the broker to magnify their Forex holdings considerably.
What is the definition of Margin?
Margin is the amount traders need to deposit in order to engage in leverage trading. It is a minimum deposit and varies from currency pair to currency pair.
What is the definition of Risk Management?
Risk management is the identification, calculation, and mitigation of risk.
What is the definition of Exposure?
Exposure is the risk involved in trading in the forex market. If you are engaged in currency trading, you are, in fact, exposed to the government policies and economies of the countries involved.
What are the Most Frequently Asked Questions About Forex Leverage?
What is a good leverage for forex?
Leverage trading starts at 5:1 and can go up to 100:1. Good leverage depends on the risks a leveraged trader is willing to take.
What does 1 to 500 leverage mean in forex?
This means that a trader can trade 500x the value of the original deposit, aka margin.
What is the best leverage for $10?
Generally, forex brokers don’t offer more than 50:1 leverage, and for good reasons. So, with $10, you can engage in leveraged trading of $500.
What is a 1 1000 leverage?
This means that a trader can engage in 1000x leveraged trades.
How much leverage for $100 dollars?
If the leverage is set at 10:1, you can leverage $1000 for $100.
Is 1/500 leverage good for a beginner?
No. A beginner should start small and slowly build.
What leverage should a beginner use?
A beginner should start with 2:1 or 5:1 leverage at the maximum and learn from it.
What is the safest leverage in forex?
The safest leverage in Forex is 2:1, so there is no risky exposure.
How much can you make with $1000 in forex?
By engaging in leverage trading, you can make $1000 every day with just $1000 in deposit, but it is risky and can result in massive losses.
Conclusion: Balancing the Power and Peril of Leverage in Forex Trading
Mastering the use of leverage is key to maximizing potential gains while minimizing risks in forex trading.
Leverage trading is a double-edged sword that should only be engaged smartly. Leveraged positions have a history of going wrong, and they are an extremely risky tool in the hands of inexperienced traders. It is important to understand them at an advanced level before engaging in high-leveraged positions.
Disclaimer
eToro is a multi-asset platform which offers both investing in stocks and cryptoassets, as well as trading CFDs.
Please note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 51% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money
This communication is intended for information and educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or investment recommendation. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Copy Trading does not amount to investment advice. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs and makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication, which has been prepared by our partner utilizing publicly available non-entity specific information about eToro.
