
Options Trading refers to a financial instrument that is based on the value of underlying securities, such as stocks, indexes, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Options trading has become one of the most popular instruments in trading in the last couple of years.
This is why the total volume of future and option trading reached 137.3 billion contracts in 2023, up 64% from the previous year globally.
I have been in the markets for more than seven years, and this is the biggest rise in numbers globally.
Options trading is an instrument in trading; options are derivatives of stocks or any other asset.
It allows investors to buy or sell the right to purchase or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe.
This article covers all you need to know about options trading in depth. But first, let’s start with the basics.
What is Options Trading, and How Does it Work?
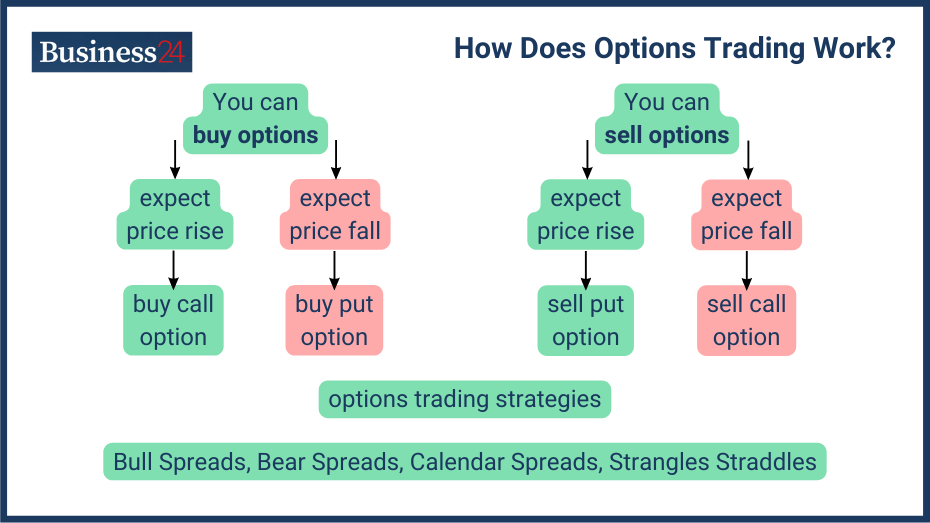
Options trading is a type of financial trading that allows traders to speculate on the future price movements of an asset without actually owning it; a trader only has to pay a premium for the contracts. This allows traders to profit from price changes, using call options to buy or put options to sell.
So, when you hold an option contract, you gain a right but not an obligation to exercise the option before it expires. You don’t have to go through with the contract if conditions become unfavorable; you can choose not to execute it.
What is an Example of Option Trading?
An example of options trading is as follows:
Let’s say you are an options trader, and you speculate a company’s stock price will rise. You buy a call option with a strike price of $50, expiring in one month, for a premium of $2 per share. If the stock price reaches $60 before expiration, you can exercise the option to buy at $50 and sell at $60, profiting from the difference minus the premium cost. So here, your profit will be $10*100 = $1000 (Option covers 100 shares). Total profit here will be $1000 – $200(premium paid) = $800.
However, if the stock trades below $50 and the option expires worthless, you lose the $2 premium. And your loss will be $200. But, before the expiration, you can close your options contract for a more minor loss or profit.
What are the Types of Options?
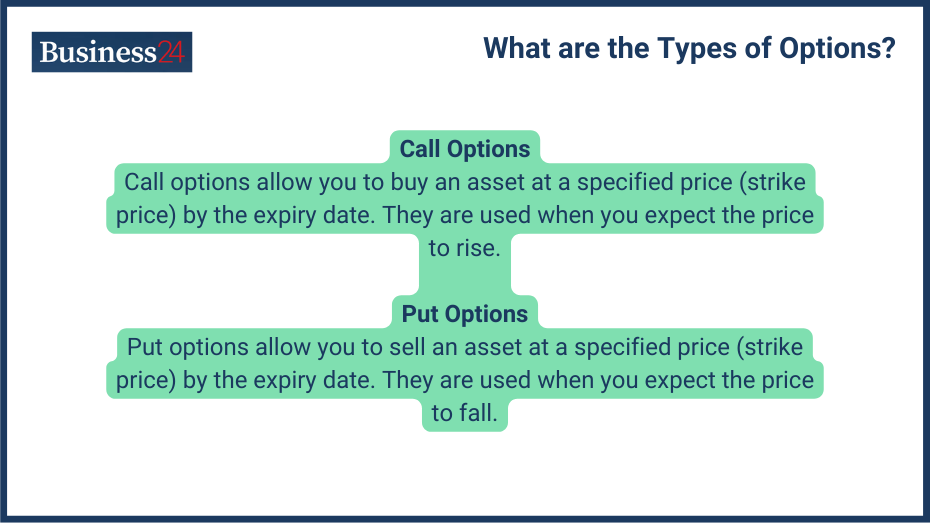
There are two types of Option Contracts:
Call Options
Call options are a type of option contract used when the price is expected to rise. They are great if you’re bullish on any asset. According to the definition of call options, they give the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset at a specific price (strike price) by the expiry date.
Put Options
Similarly, you buy a put option when expecting the price to fall. It grants the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a specific price (strike price) by the expiry date.
Learn more about writing options here.
What are the Key Terminologies in Options Trading?

When trading options, it is essential to understand the key terminologies that are commonly used:
- Strike Price: It is predetermined price at which the option can be exercised (bought or sold), think of it as the price tag on the asset.
- Expiration Date: On the expiration date, the options contracts become zero if they are not exercised.
- Premium: The cost paid to purchase an option contract.
- Intrinsic Value: The difference between the underlying asset’s current market and strike prices.
- Time Value: Time also factors in the price of an option, the additional value of the option is based on the remaining time until expiration,generally declines as expiration approaches.
How Exactly Does Options Trading Work?
Options trading involves several steps:
- Choosing the Right Option: When choosing an option, I always consider the market conditions and my own risk tolerance. Based on your analysis, whether you are expecting upside or downside momentum, you have to choose a call or put option, respectively.
- Paying the Premium: To purchase the contract, you have to pay the seller a premium.
- Exercising the Option: If your prediction is correct, you can close your position anytime you want, also if it goes against you and you want to limit your loss you can close the position anytime before expiry. And if you don’t exercise the contracts before the expiry it will go to zero and you will only lose the premium you paid for the contract.
What are the Investment Strategies with Options?
There are various types of options trading strategies, including:
- Covered Call: It is simultaneously selling a call option and holding the underlying asset to generate income from the premium while limiting potential profits from a price increase.
- Protective Put: in protective put a trader buys a put option to hedge against potential losses in an already owned asset.
- Straddle: This involves buying both a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date, profiting from a significant price movement in either direction.
- Spread A combination of buying and selling options of the same class (call or put) with different strike prices or expiration dates. It limits the risk while using leverage to profit from the price fluctuation.
What are the Risk Factors in Options Trading?
According to the studies, most traders lose money in options trading due to a lack of knowledge and risk awareness. So, it is vital to know the risk involved in options trading:
- Market Risk: No one in trading knows what could even occur the next day, accurate market prediction is nearly impossible, and various events can increase volatility.
- Leverage Risk: Options are a double-edged sword. They can make you a good profit, but you can also lose all the premium you paid.
- Liquidity Risk: It is the risk that an investor mneed more market participantsble to buy or sell options contracts quickly enough at a fair prnts. Such as wide bid-ask spreads, low trading volume, risk of unfavorable price movements, etc.
- Time Decay (Theta): With the time option, contracts lose their value; whether they move in your direction or not, they decay with time.
How Do Options Compare to Other Investments?
Here are some other alternative options:
Compared to Stocks, Options offer increased leverage and flexibility, enabling investors to hold more cons with smaller investments and take advantage of different market conditions. Stocks are a less complex and lower-risk option for those looking to invest.
Compared to Bonds, Bonds provide steady income and a return of principal upon maturity, making them safer investments. However, options are high-risk, high-return instruments.
Compared to ETFs: ETFs are used for diversification in investing; they are baskets that invest in different types of assets in different sectors. ETFs are investing instruments, while options are trading instruments.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
Options trading can be used for different goals:
Speculation: Most use of the options is in speculation industry. Traders use this instrument more often to profit from price fluctuations.
Hedging: This is like buying insurance for your investments. Hedging helps to protect you from the opposite side of your investment. For example, you have NVIDIA shares bought for investment purpose but you are expecting a big correction, so you buy put options or sell call options as a hedge to your investment.
Income Generation: You can generate income with option selling. When you sell an option, the buyer pays you a premium, which you can profit from if your analysis is right.
Educational Resources and Tools
Some of the ways to learn options trading are:
Books and Articles: Books and articles written by experts can be a great source for learning the basics and advances of options trading.
Online Courses and Tutorials: Various options trading courses and videos teach different strategies and how the options market works. Not all of them are good, but you can find some good ones through research.
Financial Tools: You can use options calculators or paper trading to see how trades might work. This way, you can gain some experience and also avoid losing any money. However, the most important part of learning is getting real experience in the market.
Should Beginners Do Options Trading?
If answering yes or no, the answer is no. Beginners should not try options trading because it requires a lot of experience and fast execution. Options are complex and risky, so learning the basics is essential.
What beginners can do is use virtual trading platforms, where they can practice without real money. It will help to understand how options work without the risk of losing money. Start with small amounts and focus on gaining knowledge and experience before investing more.
How Do Options Traders Make Money?
For an options trader to make money, he has to predict the direction of the trade correctly. After executing the options contract, the profit or loss is the difference between the strike and market prices minus the premium paid. If they predict the asset’s price correctly, they can sell the option at a profit.
For example, when buying a call option at $20, and its price rises to $25, you close the profit for $5 per contract. The important thing is to predict the price movement correctly and ensure the profit must be the option’s initial cost.
Disclaimer
eToro is a multi-asset platform which offers both investing in stocks and cryptoassets, as well as trading CFDs.
Please note that CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 51% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money
This communication is intended for information and educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or investment recommendation. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Copy Trading does not amount to investment advice. The value of your investments may go up or down. Your capital is at risk.
Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more
eToro USA LLC does not offer CFDs and makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this publication, which has been prepared by our partner utilizing publicly available non-entity specific information about eToro.